Components of C.P.U.
| Sr. no. |
Components |
Image |
Description |
| 1. |
Processor |

|
Brain of a computer that executes instructions and performs
calculations. Intel Core i5 and AMD Ryzen 5 series for everyday use 7
and 9 series for gaming and video and photo editing Quantum
processors, which use quantum physics to enable algorithms that are
impossible on classical computers Photonic processors, which use light
to make computations instead of semiconducting electronics
|
| 2. |
Storage |

|
The storage unit is a part of the computer system which is employed to
store the information and instructions to be processed. A storage
device is an integral part of the computer hardware which stores
information/data to process the result of any computational work.
Without a storage device, a computer would not be able to run or even
boot up. Or in other words, we can say that a storage device is
hardware that is used for storing, porting, or extracting data files.
It can also store information/data both temporarily and permanently.
Types of Computer Memory - Primary Memory, Secondary Memory , Tertiary
Memory
|
| 3. |
Power Supply |

|
A computer power supply is a device that converts electrical energy
into usable energy for a computer. It takes the energy from an
external source, like an outlet or generator, and transforms it into
low-voltage DC power to run the components of your computer.
|
| 4. |
Graphic Card |

|
A graphics card (GPU) works by processing and rendering images,
videos, and animations to display them on a monitor. It acts as a
mini-computer specialized in handling graphical tasks efficiently.
|
| 5. |
Cooling fan |

|
A cooling fan for the CPU is essential to keep the processor from
overheating and ensure stable performance. Here’s how it works and why
it’s important. Types of CPU Cooling Fans- Air Cooling (Most Common)
,Liquid Cooling (For High Performance)
|
| 6. |
Sound Card |
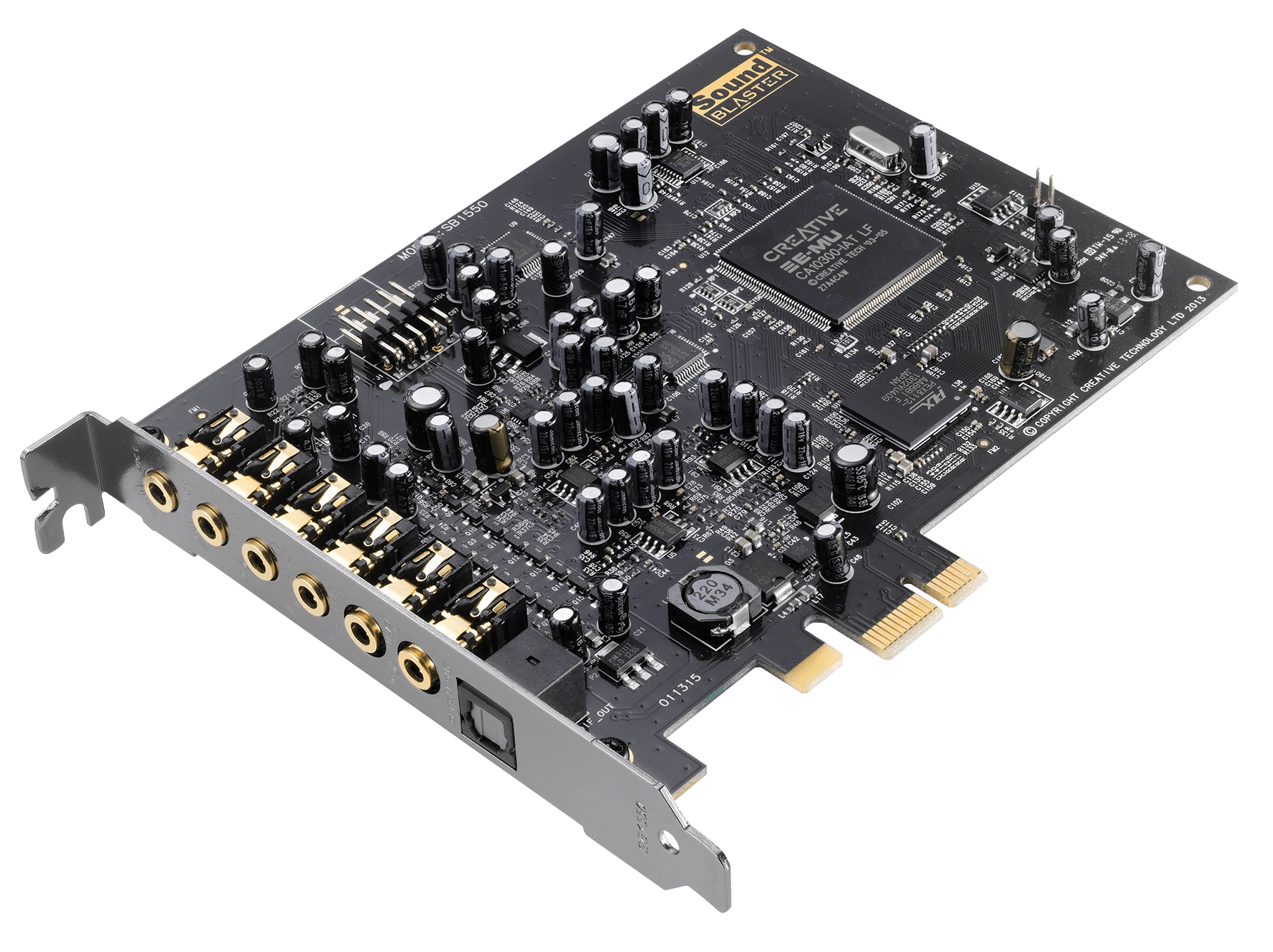
|
A sound card is a hardware component that processes audio signals and
improves sound quality for speakers, headphones, and microphones.
|
| 7. |
Motherboard |
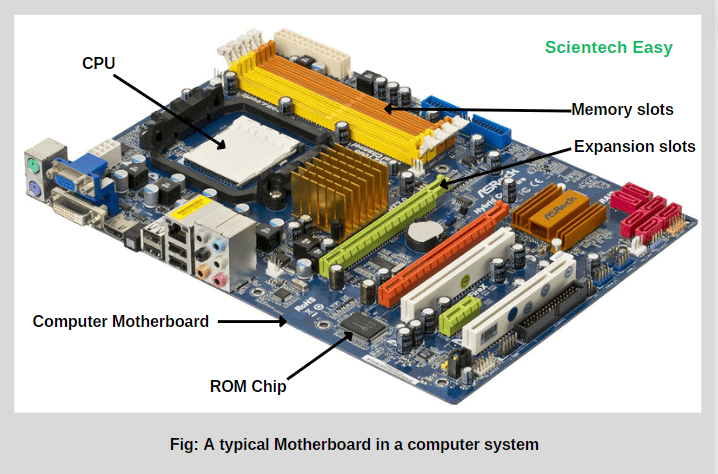
|
The motherboard is the main circuit board of a computer that connects
and allows communication between the CPU, RAM, GPU, storage, and other
components. It acts as the backbone of the system, ensuring all parts
work together.
|
| 8. |
Wifi Module |

|
The Wi-Fi module allows the computer to connect to wireless networks
without an Ethernet cable. It uses radio signals to communicate with a
Wi-Fi router.
|
| 9. |
Bluetooth Module |

|
It allows a computer to wirelessly connect to Bluetooth devices like
headphones, keyboards, mice, speakers, and smartphones. The Bluetooth
module uses radio waves to connect wirelessly to nearby devices. It
operates on the 2.4 GHz frequency for short-range communication. It
supports various Bluetooth versions (e.g., Bluetooth 4.0, 5.0, 5.2,
5.3).
|
| 10. |
Input/Output Board |

|
An I/O board, or Input/Output board, is a circuit board that allows a
computer to communicate with and control external devices, acting as a
bridge between the computer and peripheral devices like keyboards,
mice, monitors, and other hardware
|
| 11. |
RAM (Random Access Memory) |

|
RAM is a separate component installed on the motherboard in RAM slots
(DIMM slots). The CPU uses RAM to store and access data quickly while
performing tasks.
|
| 12. |
Optical Drive |

|
It is used to read and write data from optical discs like CDs, DVDs,
and Blu-rays.
|
| 13. |
USB |
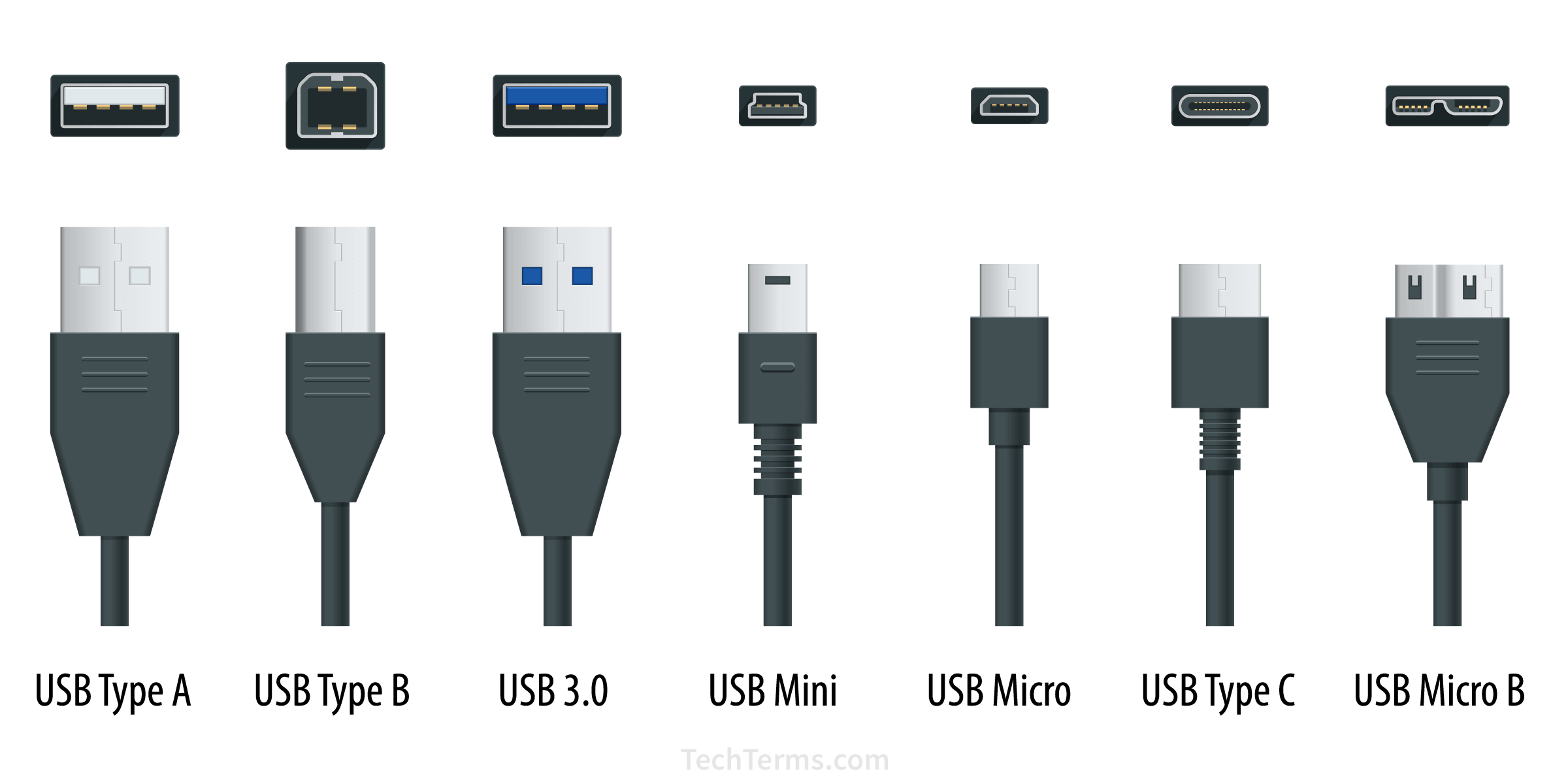
|
A USB port in a CPU is a connection point that allows you to connect
devices to your computer using a USB cable. USB ports are commonly
found on the front and back of desktop computers.
|
| 14. |
Hardware Case |

|
The enclosure that contains most of the hardware of a personal
computer.
|
| 15. |
SSD |

|
SSD stands for Solid-State Drive. It's a type of storage device used
in computers that is faster and more reliable than traditional hard
disk drives (HDDs) because it has no moving parts. SSDs use flash
memory to store data, resulting in quicker boot times, faster file
transfers, and improved overall system performance.
|











